What are SDGs?
SDG stands for Sustainability Development Goal. These were created by the UN in order to end any and all forms of poverty. Such goals include Zero Hunger, Clean Water and Sanitation, and Sustainable Cites and Communities
Image Credit: UNDP
How do Satellite Data Help Achieve SDGs?
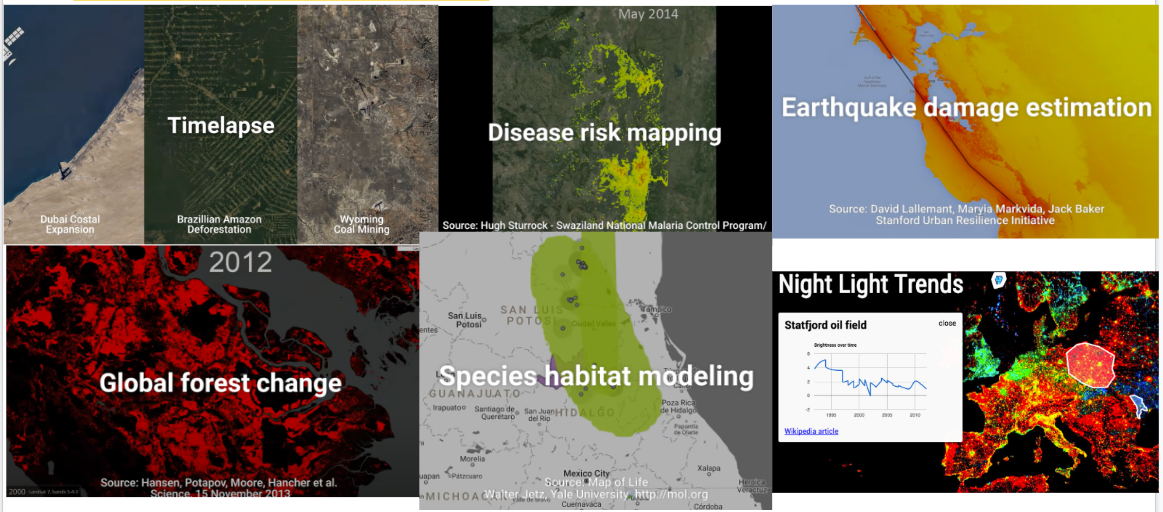
Achieving the United Nations' Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) begins with robust data collection. Satellite technology provides a powerful means to observe and analyze key global trends, including heat distribution, reforestation efforts, water flow, and watershed management. These insights enable us to assess risks, allocate resources effectively, and support impactful, data-driven initiatives that advance sustainability.
What Tools Can I Use to Learn About Satellite Data?
The Google Earth Engine, which is a cloud-based platform, is primarily used for urban planning, environmental monitoring, and other remote sensing capabilities. To see how other people have applied GEE, look at these projects below.
Ecological Quality in Chinese Metropolitan Area
Due to declining land quality as part of China’s urbanization efforts, researchers based in China sought to find the ecological quality in the Lhasa Metropolitan Area. The area is a part of the Tibetan Plateau, which is considered the ecological barrier for biodiversity and the water cycle, is susceptible to human activity and climate change. Using the Google Earth Engine to synthesize the images and calculate the Remote Sensing Ecological Index, they were able to monitor how the population growth and economic growth did not negatively affect the ecological quality, but instead boosted it. From these results, they found that GEE could be an efficient computing platform for monitoring eco-environmental quality in vast regions. To learn more about this project, click here.
Other GEE Projects
Drought Monitoring in South Africa and Ethiopia
One of the best ways to monitor drought and crop conditions are through monitoring the soil moisture. Therefore, the researchers for this study used the Google Earth Engine for its diverse array of data as well as cloud-computing capabilities, which provide better access to a wide variety of users. Using the GEE allowed them to analyze the Standardized Precipitation Index and the Normalized Difference Vegetation Index in South Africa and Ethiopia, two regions that regularly suffer from droughts. The researchers found that GEE causes more efficient drought analysis and allow for better drought preparedness. To learn more about this project, click here.
Land Cover Change over Africa
Many of Earth’s land surface processes can be better understand by monitoring the land cover change over time. However, due to the high quality of images needed and the long time needed to monitor change, high processing power computers were required to study the changes. To overcome the processing cost, the Google Earth Engine allows for users to use the cloud-computing power while not on a high processor computer. To learn more about this project, click here.